Undervolting graphics cards is a technique that can provide several benefits over simply overclocking. By lowering voltages while maintaining clock speeds, temperatures, and power consumption can be reduced. This extends component lifespan and improves sustainability.
Need for Undervolting
Lower Temperatures
Reduced voltages lower heat output, allowing lower fan speeds or smaller cooling solutions. This drops temperatures significantly under load.
Increased Lifespan
Excessive heat is a major factor in reducing part longevity over time. Lower temps from undervolting can increase the reliability and lifespan of key components.
Power Savings
Lower voltages mean less power is required to maintain performance. This results in energy cost savings and less strain on PSUs.
Performance on Ada Lovelace and RDNA3
Ada Lovelace GPUs from Nvidia deliver massive horsepower while being very power-hungry. RDNA3 offers competitive performance as well. Undervolting these provides an appealing balance of gaming prowess and efficiency.
Nvidia Ada Lovelace Performance
Testing shows even aggressive undervolts sustaining stock speeds with negligible 1-3% performance drops. Surprisingly, sometimes a slight gain is seen by lowering temperatures.
AMD RDNA3 Performance
Early results show that RDNA3 architecture also maintains stock speeds with 10-15% lower voltages. Minimal 1-2% performance reduction at most. Some workloads see minor boosts.
Undervolting on NVIDIA Graphics Cards
Unlike AMD, NVIDIA does not provide an official overclocking utility. However, MSI Afterburner is the leading third-party solution for tuning NVIDIA GPUs.
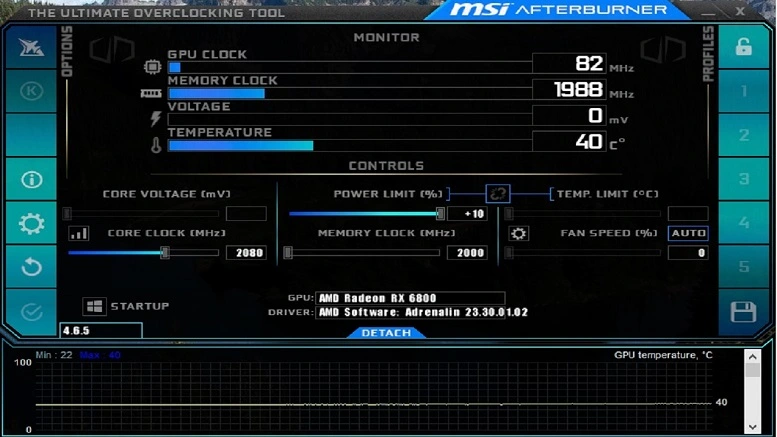
MSI Afterburner Interface
MSI Afterburner has a clean interface displaying key stats like core clocks, fan speeds, voltages, and temperatures in real time. Sliders allow adjusting these parameters for manual tweaks.
Monitoring Core/Memory Clocks
Out of the box, check stock speeds which can serve as baseline stable levels to work from during undervolting testing. Verify speeds don’t unexpectedly downclock under load.
Finding Stock Voltages
The voltage curve editor shows factory voltages at differing clock speeds. Note stock voltage levels corresponding to your card’s boost GPU clock for reference points.
Unlocking Voltage Controls
Go to settings and check the box to unlock voltage control for manual adjustments in mv steps. Finer control grants more precision.
Setting Power Limit
Raising the power limit by 5-10% provides overhead for higher clocks maintained when gaming or benching. Redundant now but safer for tweaking.
Introduction to Undervolting
Explain the concept is lowering voltage while benchmarking for stability to reduce temperatures, noise, and power consumption without losing performance.
Starting the Process
Set a target clock speed achievable at stock voltage as the goal. Gradually subtract voltage in 25mv steps and stress test each revision with benchmarks.
Stress Testing Configurations
Use tools like 3DMark, Superposition, and in-game benchmarks to thoroughly evaluate settings. Run repeated tests for at least 15 minutes each prior to labeling as stable.
Monitoring Temperatures
Key stats to watch include hotspot temperature and memory junction temp displayed. Ensure safely below 95 degrees Celsius at minimum load.
Finding the Minimum Stable Voltage
Iteratively test lower voltages until artifacts, crashes, or reduced scores occur. The final stable value yields max power/thermal reduction before instability.
Fine-tuning the Undervolt
Small repeated tweaks of voltage up/down in 10mv steps hone in on the lowest possible voltage to maintain stock clocks. Substantial improvements are achievable.
Custom Fan Curves
Adjust fan speeds manually as temperature increases using curve points for constant active cooling and lower temperatures under all conditions.
Maximizing Stability
Regular re-testing after hours/days verifies settings remain rock solid. Monitor for degradation indicating inadequate undervolt requiring small voltage increases over time.
Summary
In summary, judicious undervolting of NVIDIA RTX 40 series graphics cards reliably reduces thermals and power usage with minimal tuning using MSI Afterburner. This extends component lifespan substantially with small performance impacts for most workloads and games. With stress testing, it unlocks a low-effort path toward a more efficient and sustainable GPU tuning experience.
Undervolting on AMD Graphics Cards
Unlike Nvidia, AMD provides its Radeon Software utility for fine-tuning GPU parameters. This integrated tool simplifies optimizing RDNA3 performance.
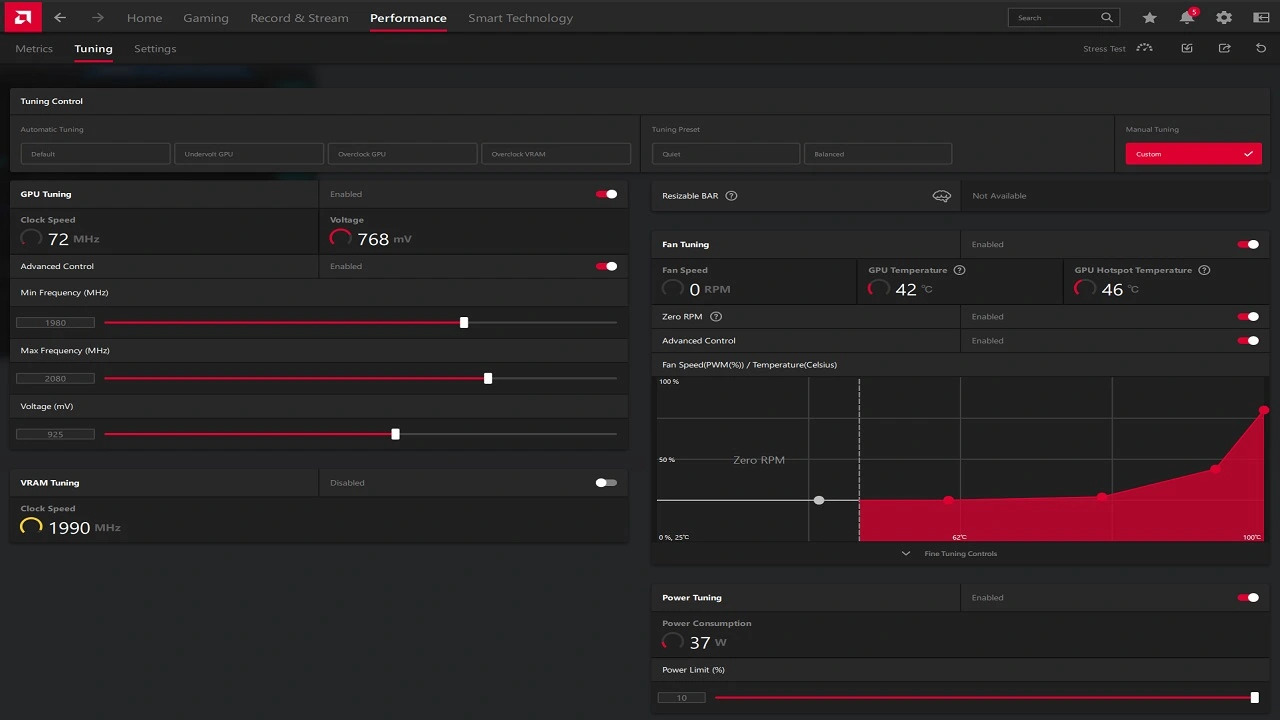
Radeon Software Interface
The software has an interface showing temps, clocks, usage, and tuning options. Key stats are monitored alongside customization sliders.
Enabling Undervolting
Under “Performance” find the “Tuning” tab revealing voltage/frequency curve and controls to manually lower voltages from stock settings.
Identifying Stock Settings
Review factory voltage-frequency curve to note reference points like minimum/maximum stable voltages corresponding to target clock speeds.
Adjusting Voltage Controls
Subtract voltage in precise 10-25mV steps using the curve editor for each targeted frequency. Monitor loading benchmarks between changes.
Monitoring Hardware
Check hotspot temperature, memory/VRAM temps, frequency, and utilization levels while benchmarking to verify safe operating conditions.
Establishing a Baseline
Run benchmark to log baseline scores at stock settings. Work towards matching this as a goal while discovering the lowest possible stable undervolt.
Iterative Testing
Methodically lower voltages and test for instability through crashes, artifacts, or reduced benchmark scores. Revert to the last known good settings on failures.
Maximizing Stability
Regularly re-test configurations over multiple gaming sessions to verify solid long-term reliability under real-world loads.
Fine-Tuning the Undervolt
When closest to stability, use smaller 5mV voltage tweaks and extended testing to dial in optimal undervolt perfectly balanced at the stability edge.
Custom Fan Cruves
If needed, adjust fans using automatic or custom curves linked to temperatures to extract max cooling from undervolted configurations.
Maximizing Potential
Pushing memory overclocks while undervolting can partially offset any minor performance hits from significant voltage reductions.
Documenting Results
Record optimized settings as Radeon Software profiles for easy application whenever needed with validated stable configurations.
Summary
With Radeon Software’s tuning interface, undervolting AMD RDNA3 cards provide major reductions in temps, noise, and power consumption, extending component longevity substantially with minimal effort for most workloads and games.
Conclusion
Overall, undervolting graphics cards from both AMD and Nvidia can yield significant benefits with little to no performance loss. By lowering voltages through tools like MSI Afterburner or Radeon Software, temperatures and noise levels are reduced considerably. This extends component lifespans and improves sustainability.
Testing shows Ada Lovelace and RDNA3 architectures are quite capable of maintaining stock frequencies with 10-15% lower voltages. The results are reduced hotspot temperatures sometimes up to 20 degrees Celsius compared to stock settings. Moreover, power consumption decreases proportionally based on voltage reductions.
For enthusiasts, undervolting unlocked by third-party or first-party tuning software provides an effective low-effort optimizing experience. It allows squeezing every last milliwatt of performance out of modern hardware through meticulous tweaking. Overall system longevity and efficiency are markedly improved through some patient experimentation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Undervolt Cause GPU Faults?
Undervolting a GPU poses no risk of permanent hardware damage. At worst, unstable undervolts may lead to driver crashes or system reboots due to reduced stability. However, modern GPUs have various safeguards to prevent faulty operation from low voltages alone. Undervolting cannot physically harm modern graphics processors in any way.
How much performance drop Undervolt Results in GPUs?
Performance decreases from undervolting alone are typically minimal, usually within 1-3% compared to stock speeds. More noticeable drops of 5-10% may occur only if pairing an undervolt with an underclock for greater stability. But merely reducing voltages with clock speeds held constant results in negligible performance impacts for most use cases and games.
Can Undervolt also increase performance in some Cases?
In rare instances, undervolting can lead to modest performance gains rather than losses. Lower temperatures from reducing voltages allow some GPUs to sustain higher turbo clock speeds for longer before throttling.







