Gamers and hardware enthusiasts have always searched for ways to squeeze out extra performance from their PCs. With the latest generation of graphics cards from NVIDIA and AMD bringing substantial gains, overclocking provides an avenue to further boost speeds and experience games at their best. Whether it’s to maintain a high framerate at higher resolutions or to gain an edge in esports titles, overclocking the GPU is an effective way to increase performance.
According to initial tests, Ada Lovelace and RDNA 3 architectures allow for respectable headroom when it comes to overclocking. NVIDIA RTX 4080 cards seem capable of 10-15% gains on average. For AMD’s Radeon RX 7900 XT, a 5-10% bump appears feasible. Parameters to pay attention to include the core clock, memory clock, voltage, and thermal thresholds. Dialing in the right combination of these settings is key to achieving maximum stable overclocks. While pushing too hard can cause instability or reduce component lifespan, a mild overclock done properly brings worthwhile rewards.
Let us look at all the technical details related to overclocking the latest graphics cards by AMD and NVIDIA.
Parameters to Look at When Overclocking the GPU
Below are the few parameters that must be checked in accordance to each other during overclocking a graphics card.
Core Clock
The core clock controls the speed of the GPU core and its various components. Increasing this leads to overall performance gains but also higher power draw. Start with small increments of 10-25MHz.
Memory Clock
The memory clock affects graphics memory speed. Raising it provides benefits in bandwidth-hungry games. Try boosting in 50-100MHz steps and stress test for stability.
Voltage
A higher voltage allows for higher clocks but increases power usage and heat. Small voltage adjustments of 25-50mV can help reach higher clocks. Don’t exceed 1.1V on most cards.
Fan Speed
Higher clocks mean more heat. Adjust fan curves to ensure adequate cooling at all times. Watch hotspot temperatures closely during stress tests.
Power Limit
Some cards have overcurrent protection. Raising the power limit by 5-10% via software lets the card draw more electricity for overclocking headroom. Higher values tradeoff stability for performance.
Temperature Target
Most GPUs throttle clocks to keep temperatures in check. Modifying target operating temperatures to up to 85°C via software alleviates thermal throttling for additional headroom.
Methodology For Overclocking a Graphics Card
These days, it’s relatively simple to overclock a graphics card compared to what we had to do a decade ago. We don’t have to cater to burning due to over-voltage and extreme temperatures as the graphics cards have safety limits. First, we will discuss how to overclock the NVIDIA graphics cards and then we will discuss AMD graphics cards.
Overclocking NVIDIA Graphics Cards
Unlike AMD, NVIDIA does not provide an official overclocking tool. MSI Afterburner is the most popular third-party software used to overclock GeForce graphics cards. It has a clean and intuitive interface to manually tweak clocks, voltages, and fan profiles.
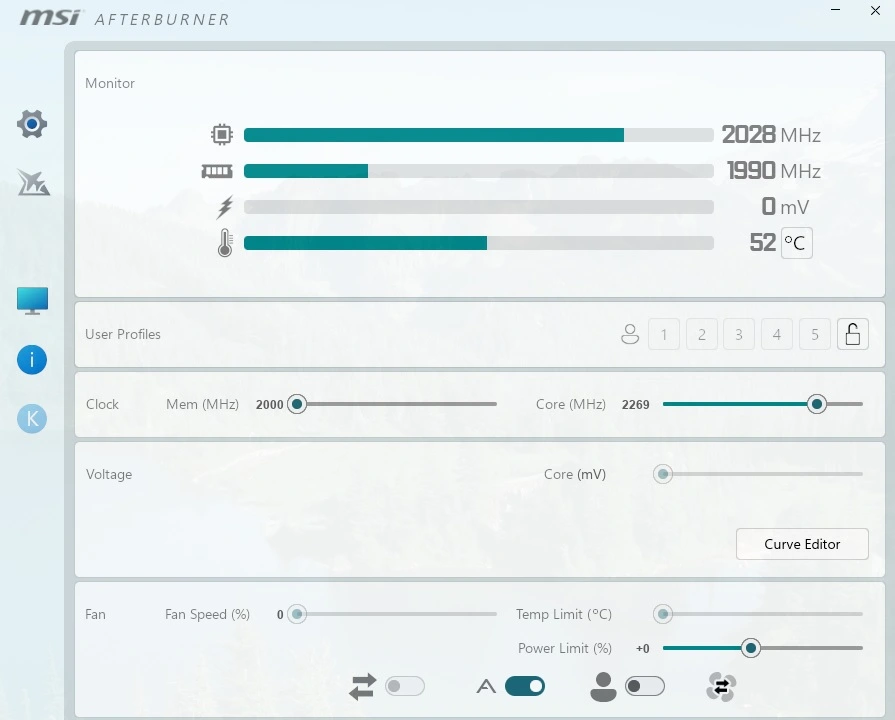
The Interface
The main window displays current clocks and voltages. Sliders allow adjusting the core clock, memory clock, GPU voltage, and power limit. A fan speed/temperature graph shows thermal readings in real time.
Core Clock
Starting from a stable stock clock, raise it in small 25MHz increments and stress test until reaching instability. Most Ada Lovelace cards can go 50-100MHz above stock speeds daily.
Memory Clock
Stock memory speeds on RTX 40 series cards range from 19-21Gbps. Increasing this by 200-500MHz is a good daily overclock range before needing more voltage.
Voltage Adjustment
Raising the voltage by small 12.5mV steps (up to 50mV maximum) allows pushing clocks higher but also increases heat and power draw. Monitor hotspot temperatures closely when adding voltage.
Fan Speed Tuning
The fan curve can be edited to dial in more aggressive cooling profiles to keep temperatures below 85°C under full-load overclocking scenarios.
Stability Testing
Use stress tests like 3DMark, Heaven, or FurMark to check for rendering errors or crashes. Run each overclock configuration through multiple test loops before considering it stable for daily use. Repeated testing ensures long-term resilience under pressure.
In summary, MSI Afterburner allows squeezing impressive extra gaming performance while manually overclocking powerful Ada Lovelace GPUs within safe parameters. With some trial and error, it can help extend their capabilities.
Step-by-Step Process For Overclocking NVIDIA GPUs
- Install MSI Afterburner and launch it. Go to Settings > General and check the “Unlock Voltage Control” box.
- Switch to the OC Scanner tab and click “Start” to let Afterburner automatically find a stable core overclock.
- Once complete, switch to the main interface. Make a note of the recommended core clock speed.
- Manually increase the memory clock by 100MHz and apply the changes.
- Run a stress test like 3DMark to check stability. If it crashes, dial down the memory clock in 25MHz decrements.
- Once stable, increase the power limit by 10% and raise the voltage by 12.5 mV. This allows for higher sustained clocks.
- Attempt increasing the core clock by another 25MHz increment. If unstable, reduce by 25MHz and test again.
- Repeat increasing/testing the voltage, core, and memory clocks in small amounts until reaching your card’s limits or thermal/power caps.
- Fine-tune fan speeds using the curve editor to keep temperatures below 80°C under load.
- Verify long-term stability through extended gaming sessions before applying the overclock as your daily profile.
- Regular stress testing prevents issues down the line. Monitor temperatures closely throughout overclocking.
Overclocking AMD Graphics Cards
Unlike NVIDIA, AMD provides the free AMD Adrenalin software for officially overclocking its GPUs. It has a dedicated tuning tab for manual tweaks and monitoring performance.
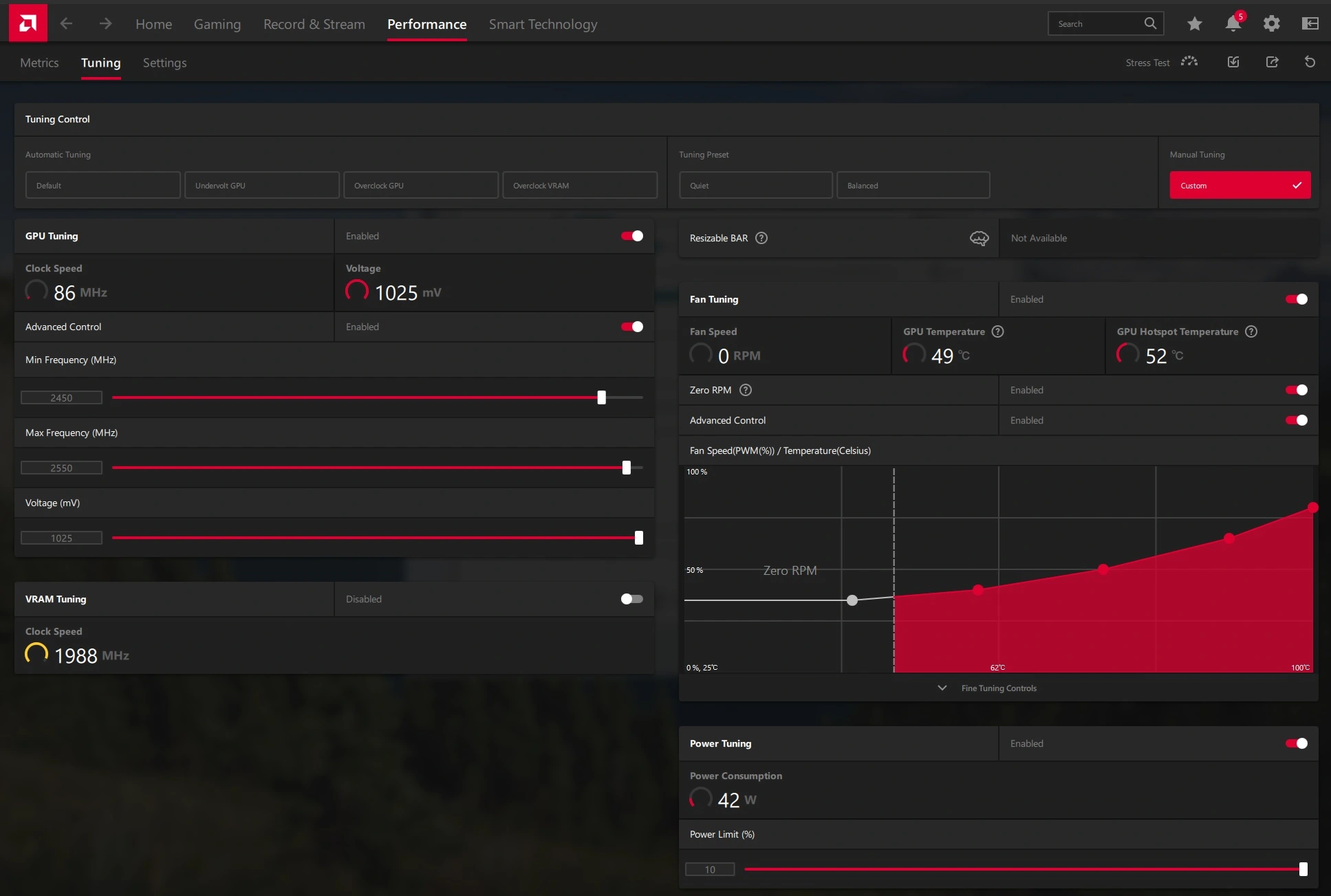
The Interface
The tuning interface displays clock speeds, fan speeds, voltages and temperatures in real-time. Sliders allow adjusting core and memory clocks along with the voltage and power limits.
Core Clock
Starting at stock speeds, raise the core clock by 5% increments and run stress tests until crashing or reaching temperature limits. RDNA3 cards seem capable of 10-15% boosts on average.
Memory Clock
Factory memory speeds vary from 16-18Gbps. Increasing this by 200-500MHz yields benefits before needing extra voltage. Test stability with each change.
Undervolting
Reducing voltages using fine-grain 0.025V steps can avoid hitting power limits, thereby allowing higher sustained clocks surprisingly. Monitor for lost stability.
Hotspot Temperature
This signifies the hottest part of the GPU die. Maintaining this under 95C unlocks full overclocking potential. Tweak fan curves accordingly.
Custom Fan Curves
The fan speed can be independently set as the temperature rises to keep components cool. Steeper fan profiles give more thermal headroom.
Benchmarking
Tools like 3DMark, Superposition, and games test stability. Run each configuration continuously for 10 minutes minimum before considering it fully stable.
Profile System
Overclocking settings can be saved as install-free profiles to apply the optimal tweaks on demand, or for easily sharing results online.
In summary, AMD’s software enables effortlessly maximizing RDNA3 performance through automated fine-grained overclocking backed by real-time hardware telemetry.
Step-by-Step Process For Overclocking AMD GPUs
- Open the Radeon Software and click the tuning tab. Set all sliders to their default positions.
- Increase the power limit by 5-10% to allow for higher clocks under load.
- Raise the core clock by 5% increments and apply the changes.
- Run a stress test like 3DMark to validate stability. If unstable, reduce the core clock.
- Once the core clock is stable, increase the memory clock by 150-200MHz.
- Test again until you encounter crashing or artifacts in benchmarks.
- If unstable, lower the memory clock slightly till it’s rock solid.
- Try increasing the core voltage within safe limits to push clocks higher.
- Monitor hotspot temperature and tweak fan speeds if needed using custom curves.
- Repeat increasing/testing clocks, and voltage gradually until thermal/power thresholds.
- Export your overclocked profile for easy application later on.
- Verify long-term stability through gaming sessions before daily use.
- Regularly stress-testing individual parameter changes is key to finding the optimal stable overclock.
Conclusion
Both AMD and NVIDIA GPUs can experience worthwhile performance boosts through considered manual overclocking. While not an essential process, it allows squeezing extra frames per second for smoother gaming. The built-in utilities like AMD’s Radeon Software or third-party options like MSI Afterburner enable efficiently pushing modern graphics cards to their limits.
By methodically stress testing small adjustments in key clock speeds, voltages, and cooling, stability can be validated for daily desktop use. With some experimentation, overclocking remains a fun way for hardware enthusiasts to maximize their investment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which software is better for overclocking NVIDIA GPUs?
Nvidia does not provide an official overclocking software. For overclocking Nvidia GPUs, MSI Afterburner is considered the best 3rd party solution. MSI Afterburner has a very user-friendly interface that makes overclocking easy. It allows adjusting core clocks, memory clocks, fan speeds, and voltage with great precision. Its widespread use and active development make it a very reliable choice for overclocking Nvidia graphics cards.
Which software is better for overclocking AMD GPUs?
AMD provides its own Radeon Software for overclocking its GPUs. The built-in overclocking utility is far more advanced than third-party solutions like MSI Afterburner for overclocking AMD graphics cards. Radeon Software allows precise per-component tuning along with real-time hardware monitoring.
Can we burn the graphics cards during Overclocking?
Modern graphics cards have extensive safety features that make it practically impossible to damage the hardware through overclocking alone. They have precautions like voltage throttling, current limits, and thermal throttling to prevent damage from overvolting or overheating. While pushing the limits may crash the driver or blue screen the system, it will not allow burning or ruining the GPU.







